“Too err is Human: Building a Safer Health System”
The title that shocked the healthcare when Institute of Medicine reported that adverse events were the leading cause of death. It is difficult to think that seeking help caused more damage than good. The change began and continue to evolve to make healthcare a safer place with emphasis on errors which occur due to negligence and can be prevented.
Not so long away, a wrong patient was operated on the leg when he was admitted for head injury. Result, patient underwent an unnecessary procedure, has difficulty walking and still left untreated. In this case, the doctor was blamed for the mishap and was barred from operating without supervision. But the question is, was there no one else who had seen the patient before? The nurse who sent the patient for surgery, assistant who transferred the patient or the operating team (junior doctors, nurses)? The answer is complex but since it was a serious adverse event which caused grave damage to the patient, it was highlighted and the one who had the responsibility (surgeon) faced litigation.
Every day such events happen labelled as ‘Adverse events’ but often go unreported with a fear of consequences one might have to face.
‘Adverse’ a word which is frightening when attached to any situation especially in healthcare where the possibilities are enormous and tosses the mind in all sort of directions when we talk about the word ‘Adverse events’. Nurses are involved in most of the patient care delivery services whether in-patient, outpatient, community health care, name it and nurses are there managing patient independently or assisting doctors to do so.
10 facts on patient safety- An eye opener on adverse events (WHO)
- Patient harm is the 14th leading cause of global burden of diseases
- While in hospital, 1 in every 10 patients is harmed
- Unsafe use of medication harms millions and costs billions of dollars annually
- 15% of hospital spending is wasted dealing with adverse events
- Investments in reducing patient safety incidents lead to financial savings
- Hospital infections affected 14 out of every 100 patient admitted
- More than one million patient die annually from surgical complications
- Inaccurate or delayed diagnosis affects all settings of care and harm an unacceptable number of patients
- Overall medical radiation exposure increase is public health and safety concern
- Administrative errors account for up to half of all medical errors in primary care
What are the types of adverse events in healthcare?
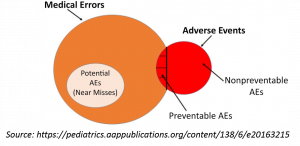
- Adverse event- It is an injury that happens to the patient in healthcare and is related medical management that results in measurable disability, prolonged hospitalization or both. The cause of such adverse events however may not always occur as a result of error on the part of healthcare provider. A common example is adverse drug reaction which is unexpected reaction to a drug administered for therapeutic purpose. Adverse event caused by errors may include:
- Commission errors- These include errors which occur as a result of doing something wrong. A common nursing commission error would include administering wrong medication dose to a patient.
- Omission errors- These errors include the either delay, partially completed or incomplete care that a patient should have received. For example the most common missed nursing care aspects are ambulating a patient, giving mouth care or turning a patient which could lead more grave consequences such as development of pressure ulcer or pneumonia in ventilated patient. Read more here: https://psnet.ahrq.gov/primers/primer/29/Missed-Nursing-Care
- Error- It is the failure of a planned action to be completed as intended called the error of execution or the use of a wrong plan to achieve an aim called the error of planning. Number of error happening in healthcare may be large so these errors are classified as the one which are potentially harmful (such as near misses).
- Near miss- It is a serious error that could have caused an adverse event, but did not occur as it was detected or was interrupted. It is encouraged that a near miss event be reported as no harm was done to patient and the healthcare provider will not face in litigation.
- Hazards and unsafe conditions- These refer to reporting of hazards that may happen for example look alike and sound alike medicines.
Types of Adverse events in direct nursing care
As per the literature, the following are the most common types of adverse events reported in direct nursing.
1. Adverse events related to medication administration- One of the commonest type of adverse event. The possibilities of adverse events related to medication administration include:
- Omission of medicine
- Miscalculation of dosage
- Errors during medicine administration
- Inadequate dosage of medicine
- Technical administration errors
Learn more about medication safety here:
2. Adverse events related to the monitoring of patient- These events happen as a result of lack of adequate monitoring of a patient which demands nursing attention. These include:
- Patient fall
- Displacement of catheters, tubes or drains
3. Adverse events related to the maintenance of skin integrity- Pressure ulcers and disrupted skin integrity of a patient is always directly associated with faulty nursing care. These events include:
- Pressure ulcers as a result of lack of position change and inappropriate position in bed.
Learn more about pressure ulcer care here:
/product/care-of-patient-with-pressure-injury-bed-sore/
4. Adverse events related to material resources- These are the events which are preventable to quite an extent with efficient management and ensuring quality resources in patient care. Examples of these events related to material resources include:
- Adverse event due to lack of equipment
- Adverse event due to defective equipment
Are sentinel event and adverse event same?
Those of you who have participated in the process of accreditation especially Joint Commission International (JCI) must have heard the term Sentinel event. So, is it the same as adverse events?
Sentinel event- JCI defines sentinel event as an unanticipated death or loss of function unrelated to the natural course of the patient’s illness or underlying condition or wrong-site, wrong-procedure, wrong-patient surgery. It is called sentinel because it signals a need for an immediate investigation and response.
Sentinel Event= Adverse event + Near Miss
Sentinel event combines adverse event and near miss and covers the full range of undesirable events with varying degrees of serious outcomes.
Most commonly reported Sentinel events
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) maintains database for the most commonly reported sentinel event which include the following:
- Patient suicide
- Operative/postoperative complication
- Wrong-site surgery
- Medication error
- Delay in treatment
- Patient fall
- Patient death or injury in restraints
- Assault, rape, or homicide
- Transfusion error
- Perinatal death/loss of function
Evidence based Patient Safety Intervention
The following are evidence based safety interventions based on extensive review which can prevent sentinel events in patient admitted in hospital.
- Guidelines- Follow antibiotic guidelines to prevent pneumonia and reduce mortality rates.
- Protocol for catheter insertion and maintenance- Catheter-associated urinary tract infection is a preventable event in healthcare setting. It can be done by giving catheter reminders and stop orders as soon as the requirement is not there. Nurses should be made in charge of assessment and suggest decisions when a patient does not need a catheter.
- Use of care bundles- Care bundles to reduce rates of central-line-associated blood stream infections (CLABSI) are encouraged and are known to influence the rate of CLABSI. Similarly care bundles for other hospital acquired infections.
- Use of Clinical pathways to avoid complications is encouraged. Clinical pathways are evidence based set plan of care involving a team of professionals (doctors, nurses, dietician, and physiotherapist) with defined time frames and expected outcomes for a particular disease condition.
- Promoting multidisciplinary team collaboration and interventions to reduce mortality rates.
- Multi-component interventions for reducing events like falls and delirium.
- Encourage exercises to reduce risk of falling.
- Regular review by pharmacist in the clinical areas to prevent adverse events related to medication and to control medication errors.
- Increase number of trained support staff to reduce mortality.
- Nurse-led early-discharge programmes to reduce mortality rates.
- Creation of rapid response team with defined roles to manage cardiopulmonary arrest.
- Surgical safety checklist to reduce the risk for surgical-site infections and reduce mortality rates.
What to do if the adverse event has happened?
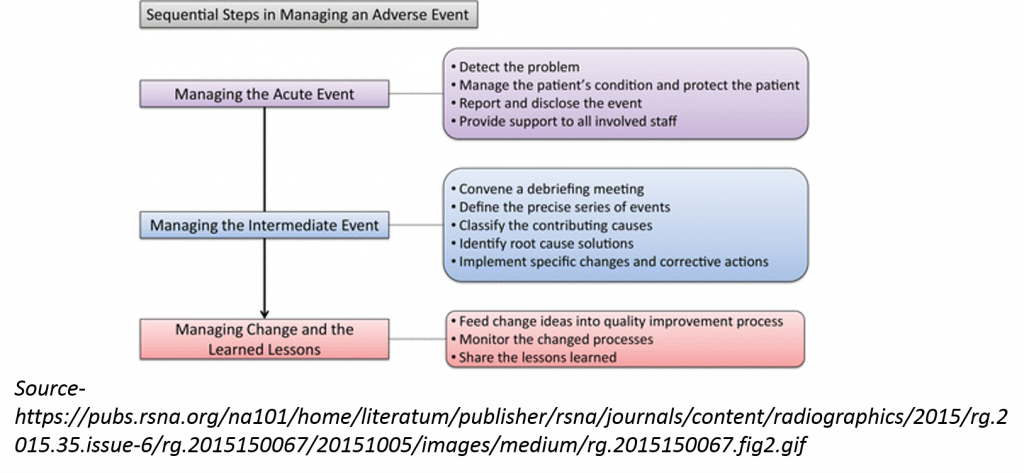
Despite all the efforts there are times in clinical setting that adverse events happen and the nurse leaders need to take actions. The following image shows the possible sequence of action that must take place to ensure patient safety and to understand what precautions to take next when managing a similar case next time.
How to encourage adverse event reporting?
1. Positive reporting system- A positive atmosphere can promote increased reporting by the health professionals. It is the responsibility of top leaders to encourage professionals to report events and near misses without being fearful about negative consequences.
2. Educate- Organization must ensure regular sessions are organized as per the scope of errors they might come across during patient care, their responsibilities and clinical protocols that must be followed in adverse events.
3. Anonymous reporting and use of software- Anonymous reporting can be encouraged through placement of boxes or use of software for error reporting that a user can report on without disclosing their identities.
Learn more about encouraging reporting adverse event here:
Root cause analysis
As the name indicates, earlier root cause analysis was introduced in healthcare to analyze the serious adverse events. Usually, the purview of quality team in a hospital setting now involves the team altogether to understand the sequence of events that lead to a particular event.
An example from a real scenario:
A 50 year old patient collapsed in an OPD setting and suffered a cardiac arrest. The only nurse posted in the area approached the patient and started CPR. Code blue was activated eventually and crash cart was brought located on another floor of OPD. Patient could be revived but suffered complications due to delay in first aid.
Root cause analysis was done and it was found that due to delay in receiving the team support and arrival of crash cart, patient suffered complications. What we learnt from this?
- More crash carts were installed.
- Support staff were trained in CPR in all areas and trained how to assist in using a crash cart in both inpatient and OPD setting.
- A team of professionals from the OPD to respond to Code blue was chosen as OPD and inpatient buildings were separate buildings.
Scenario two, same institute:
Another patient suffered an arrest in basement of inpatient building, where patient was undergoing a diagnostic tests. Technician and nurse manage patient. Patient is revived without any complications.
Take away:
One adverse event helped improve overall revival rate in the hospital and enhanced patient safety through the process of root cause analysis and implementation of solutions proposed.
Conclusion:
Adverse events are unfortunate but can be avoided with mutual team cooperation without blaming anyone. Hold your team together, you don’t know who will save you next. Remember before ‘REACTING’ to what your nursing team did wrong, understand how terrible must a person have felt after committing that error and he/she as healer caused more harm to the patient. See the link ‘When nurse becomes victim’-
References:
1. Institute of Medicine. To err is human: building a safer health system. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1999.
2. Brennan TA, Leape LL, Laird NM, Hebert L, Localio AR, Lawthers AG, et al. Incidence of adverse events and negligence in hospitalized patients: results of the Harvard Medical Practice Study I. N Engl J Med 1991;324:370-6
3. World Health Organization. 10 facts on patient safety. Available from: https://www.who.int/features/factfiles/patient_safety/en/
4. Directorate General of Health Services Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India. National Consultation Workshop on Patient Safety. 2010 May 10-20. Available from: https://www.nabh.co/Images/PDF/patientsafety.pdf
5. Duarte Sda C, Stipp MA, Da Silva MM, De Oliveira FT. Adverse events and safety in nursing care. Rev Bras Enferm. 2015 Jan-Feb;68(1):136-46, 144-54. doi: 10.1590/0034-7167.2015680120p.
6. Ostenberg PR, Reis P. Understanding and Preventing Sentinel and Adverse Events. ICU Management and Practise. 2008; 8 (2).
7. Nursing2019. 10 most common sentinel events. 2004 Nov; 34 (11): 35.
8. Zegers M, Hesselink G, Geense W, Vincent C, Wollersheim H. Evidence-based interventions to reduce adverse events in hospitals: a systematic review of systematic reviews. BMJ Open. 2016; 6(9): e012555. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012555
9. Kang JH, Kim CW, Lee SY. Nurse-perceived patient adverse events and nursing practice environment. J Prev Med Public Health. 2014; 47(5): 273-80.