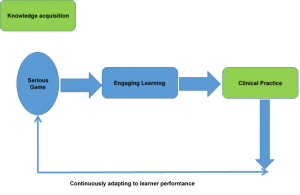
Nursing being a skill based profession we as professionals often fight to maintain the desired levels of expectations. Still struggling to maintain the quality of nursing institutes providing education par excellence to premier institutes and practical exposure to nursing students during their undergraduate days is questionable. Result is, once the nursing students graduates and enters the real practice setting, outcomes are disappointing sometimes.
As educators and nurse administrators we need to question back ourselves what exactly are we looking in our newcomers entering the system? After extensive brainstorming we bring to you the top nursing skills absolutely crucial for a new nurse.
1. Interpersonal skills (Communication)
Cliché it might sound to many, this is an important skill for a nurse while entering the system. It is an indispensable skill for a new nurse.
Though use of therapeutic communication is long been emphasized in nursing, it is seldom that we get to see it being practically implemented.
Here are some of the situations where the new nurse might need to interact and use her/his interpersonal skills.
- Nurse- Nurse (team) interaction- before even jumping on the obvious (patient nurse relationship), nurse- nurse interaction is important. How? As a new nurse, orientation to the setting where she is going to work is a challenge. A vast study conducted to acknowledge the issues of newly graduated nurses reported that nurses were able to ask for help from colleagues only 44.5% of the time. Which is quite a skewed response and shows the lack of confidence to communicate effectively with peers and seniors. Too many stimulus at the new place, people and a set of responsibilities to be fulfilled in a systematic way.

Quoting from the same study.
“As a new R.N., I worked one night with another new R.N., a more senior R.N., and a nurse leader. The two experienced nurses were far short of helpful with anything, particularly two specific patients in dangerous conditions. Both I and the other new R.N. were challenged in finding ways to report the lack of support and leadership we received that night. We asked for help and did not receive it. We struggled in professionally communicating the situation to our manager.”
Read more here: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/4dbb/f87971de24bfa66097d62a8f2860199090c6.pdf
Following are the examples of some of the communication tools nurses can use to have clear interaction about a patient. Undergraduate nursing students are taught communication skills theoretically but practical tools must be introduced early and they must be encouraged to practice it in simulated situations or with patients when practicing in clinical settings.
o SBAR- Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation
o ISBAR- Identify, Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation
o I PASS THE BATON

- Nurse patient interaction- nurse patient interaction is the core component that may attribute to patient betterment and successful clinical outcomes. See link to know more about therapeutic nurse patient interactions. https://study.com/academy/lesson/therapeutic-communication-in-nursing-examples-techniques.html
Example of how student nurses can be taught the ‘ABCDs’ of initiating an interaction is shared here.
https://journals.lww.com/nurseeducatoronline/Pages/videogallery.aspx?videoId=62&autoPlay=true.

Many such simulated scenarios must be created so that new nurses must have some clue how to react in specific situations. It is also emphasized that nurses must provide patient centered care. WHO recommends that it is important that patient is also involved in own care which impacts care component as well as better and sensible use of resources available. Learn more here:
2. Updated Practical skills
practical skills are of utmost importance. Understanding a skill is imperative but implementation is a task in itself. Nursing practice undergoes changes alongside the changes in medical system. Average life of medical information is two years which means the practices related to medical conditions will differ from what a student learns in her/his first year of nursing education. The second issue is, whether as a nurse you are able to plan, implement and evaluate the care to provide holistic care to the patient. As per an Australian study this was rated as one of the top skills a nursing graduate must have, to succeed clinically.

Another study reported that the newly graduated nurses who enter the work place are not confident to practice as they find the ‘dynamic clinical environment’ intimidating. And suggest that the institutes must provide the nursing graduates the support they need for this transitional phase in nursing. So though, the nurse managers look for the practical skills among the new nurses, they need to provide support to them for the initial few months of practice as it is not just the skills that are enough, the new nurses also need to understand a lot about the work environment and people they work with. But basic practical skills are a must, a strong educational base might help them to adjust better. An effort is required on the part of newly graduates to update themselves to the best practices in the field. An effort is required at your on level to keep up with the latest changes in practice.
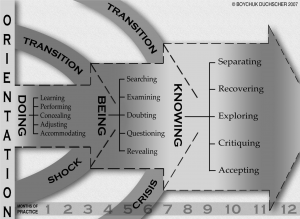
The figure above indicate the concepts of the stages of transition theory. During the initial 3 months of entering in the clinical setting, the newly graduate nurses take time to adjust to reality with emphasis on various aspects such as adjusting to the new environment and fitting in their new role. A significant change happen during 5-7 months when things start to make sense for them and they try to fit in. They may suffer from crisis situation due to lack of clinical knowledge and trying to understand everything which is going around. After 7 months, as the newly graduates move further they tend to settle in as they become more familiar with the environment, they know what to do/not to do and participate more openly in clinical care. It is thus challenging for them for the first year to adjust in the setting they work.
3. Critical thinking skills
At every step nurses come across situations where they need to make difficult choices and think straight to tackle the circumstances. Critical thinking in nursing often referred to ‘problem solving’ and ‘clinical decision making’, where the later is more intensive process involving an argument about the choice of solution or options available to address the problem. The curriculum often lack the encouragement of critical thinking skills among nursing undergraduates.
“A study assessed the critical thinking skills of fresher and senior nursing students and found that both the groups lacked critical thinking skills.”
Some of the critical thinking skills that nursing students must be trained during studies identified are (Source- Papathanasiou IV, 2014):
- Critical analysis
- Introductory and concluding justification
- Valid conclusion
- Distinguish facts and opinions
- Evaluate the credibility of information sources
- Clarification of concepts and recognition of conditions
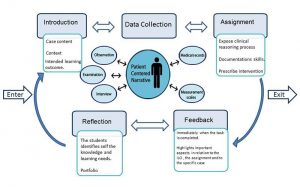
An encouragement and specific case based methods may be utilized well to promote critical thinking skills amongst graduating professionals during the nursing education. As shown in the figure, learners looks at a clinical situation from various perspectives. They notice as well as interpret what the situation is and then propose how it can be managed better. Various resources are utilized for analysis of present situation followed by assignment and feedback towards the solutions or interventions that might have improved the current situation proceeding to the last step, reflection where student is encouraged to identify what they gained and what they need to learn further.
4. Professionalism
The word ‘Professionalism’ is associated with nurses like an electromagnet. It comes with quite a number of responsibilities. The three important aspects which I found interesting are quoted here:
- Cognitive dimension- it says, the nursing educations must develop professional knowledge, which means the education must supplement the knowledge what is expected of you as a professional?
- Attitudinal dimension- one of the tricky domains to conquer, attitudinal domain is influenced by number of factors such as
- Personal features- ability to understand feelings and problems of others, willingness to help others, ability to work with others, tolerance and flexibility in communicating with others.
- Knowledge based features- knowledge, scientific accuracy and the ability to research.
- State dependent properties- willingness to take responsibility and emphasizing on the attractive external appearance.
- Psychomotor dimension- in simple words the phrase used to describe is ‘knowledgeable doer’. Arguments have it that, senior clinical nurses emphasize more on ‘doing/doer’ part of it and those holding higher degree (master’s) emphasize on ‘ knowledge’ as evident by a study conducted by Drennan J, 2009. Definition might be different but psychomotor skills are important components that in many situations do represent professionalism than the other domains.
5. Cultural awareness and ethical care
Ethics are moral principles that impacts one’s behavior. Cultural awareness is one of the top rated skills that is expected to be part of training of a graduate nurse. With India being a diverse country, it becomes important that nurses are trained, how to practice and provide culturally appropriate care. For example in Indian context, the practices, belief system, rituals, religion and health seeking behavior is different among communities which might impact the concepts of wellness or sickness and definition of health.

Here is an example:
Case study
A girl, 23 year-old, female presents with episodes of anxiety, accompanied by feelings of impending doom, shortness of breath, palpitations and loss of sensation in her limbs lasting for 15-20 minutes. The symptoms were accompanied by a shift in consciousness whereby ‘ancestral spirits’ appear takes control over her body. This experience was accompanied by violent behavior, a change in voice and irrelevant speech content, as well as general weaknesses, body aches and decreased appetite. She was reluctant to seek psychiatric help, partly because of the stigma attached to this kind of therapy.
The girl was treated and stressors were identified. She did not want to get married and was unable to convey this to her parents or express her desire to do further studies. She felt it would be disrespectful towards her parents to talk openly about such matters. At the consultation it was thought that subconsciously she was using denial and dissociation to cope with stresses arising from her internal conflict. She was eventually admitted to a local hospital for psychiatric observation and ‘distraction therapy’.
As part of nursing studies, nursing students must be given a chance to interact with diverse population with whom they are expected to work with in future. Promotion of medical tourism in India, make it more vital for the future nurses to understand the meaning of ‘transcultural nursing’. Sadly, Indian culture impact in nursing care is discussed at international level but we as natives are not yet oriented to culture sensitive care. Theoretical concepts exist but we need to wake up to improve our orientation to culturally sensitive care. See link here:
To Conclude
New nurses are expected to be skillful in many aspects of care. All nursing students preparing to graduate can do is, be oriented and updated. And remember that most nursing skills are learnt with practice so keep up your pace with the world.
References:
- Brown RA, Crookes PA. What are the ‘necessary’ skills for a newly graduating RN? Results of an Australian survey. BMC Nursing (2016) 15:23. DOI 10.1186/s12912-016-0144-8
- Duchscher JB. A Process of Becoming: The Stages of New Nursing Graduate Professional Role Transition. The Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing · October 2008 · Vol 39, No 10.
- Lippincott solutions. Turning New Nurses into Critical Thinkers. Wolter Kluwer. 2018 June 5.
- Papathanasiou I.V., Kleisiaris C.F., Fradelos E.C., Kakou K., Kourkouta L. Critical thinking: The development of an essential skill for nursing students. Acta Inform. Med. 2014;22: 283–286. doi: 10.5455/aim.2014.22.283-286.
- Kim C, Lim B. Modernized education of traditional medicine in Korea: Is it contributing to the same type of professionalization seen in Western medicine? Soc Sci Med. 2004;58:1999–2008.
- Ghadirian F, Salsali M, Cheraghi MA. Nursing professionalism: An evolutionary concept analysis. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2014;19(1):1–10.
- Drennan J, Hyde A. The fragmented discourse of the ‘knowledgeable doer’: nursing academics’ and nurse managers’ perspectives on a master’s education for nurses. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2009 May;14(2):173-86. doi: 10.1007/s10459-008-9102-x.
- Worthington RP, Gogne A. Cultural aspects of primary healthcare in India: A case- based analysis. Asia Pac Fam Med. 2011;10(1):8. Published 2011 Jun 16. doi:10.1186/1447-056X-10-8.