“Serious games are designed to achieve an intentional purpose of learning, behavioral changes in fields like healthcare where the aim is to map back learning or training objectives.”
Lately, gamification has been introduced into healthcare as it is one of the safest ways to encourage desired behavior using game mechanics.

Source: https://1712507217.rsc.cdn77.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/gamification-in-healthcare.jpg
Why Games?
Gamification has several advantages that can benefit healthcare.
- Improves retention: Games might help in better retention of knowledge as multiple senses are involved. In a study conducted by Magennis & Farrell in 2005, it was reported that retention rate was better in students who learnt by doing (75%) as compared to students who attended lectures (5%). Another study by Joyce in 2005, revealed that retention rate was maximum among learners who learnt by simultaneously seeing, hearing and doing (90%), followed by those learners who learnt by doing (80%), learners who learnt by seeing (40%) and lastly learners who learnt by hearing (20%).
- Bridge gap between theory and practice- In nursing it is often a concern to bridge the gap between theory and practice in certain concepts where it is difficult to understand if the seriousness of the situation is not highlighted. Games can encourage the learner to understand the importance of the specific action they might take and how it can affect the patient. Here is an example of a serious game called virtual pain manager which teaches nursing students the relevance of pain management. Read more here: http://vpm.glam.ac.uk/

Source: https://helsinkismart.fi/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/CareMe_1-1.jpg
- Critical thinking skills- It becomes challenging in skill based profession such as nursing to encourage the students and professionals to critically think in every possible context. Games can help the nursing professionals to apply the acquired knowledge in different clinical situations. There are games that encourage nurses to practice assessment, prevention and treatment of patient health conditions related to patient skin integrity and pressure ulcers. Huang LY in 2017, reported that students significantly improved their critical thinking skills and dispositions through the gamified platform with the experimental instruction in a blended learning environment.
- Simulate difficult real life situations- Games can not only mimic real life situation but they can be used to simulate real life situations which are difficult to create practice skills and can be even repeated if the user wants to practice for example fire safety, infection hazards etc. Pront L in 2018, concluded that the games had potential benefits of decision-making, motivation, repeated exposure, logistical and financial value.
Bodhi’s Approach to Gamification
- User centric design- Keeping the user at the core of game design process is a philosophy we follow at Bodhi. For the game to see successful adoption, it is utmost important that we know the target users well. This includes having deep knowledge about their demographic, social and cultural behavioral traits. Addressing questions like the type of context, how to implement the game for the first time and how to continue the game in future, early on can bring great clarity to the actual development process.
- Real life simulations to enhance critical thinking- Real-life patient cases can be gamified which helps in testing ‘application of knowledge’ and ‘problem solving’ rather than passive learning.
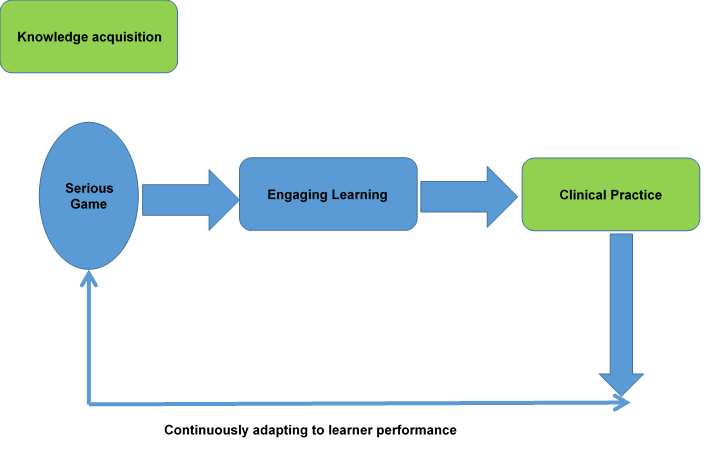
- Adaptive data driven learning- The key advantage learning technologies bring to the table is the fact that the learning outcomes can be measured to great amount of granular details. Crucial learner data such as time spent on the modules, scores obtained, past performances can reveal insights to strong and weak clinical areas requiring improvements thus helping personalize the learning outcome for every learner.
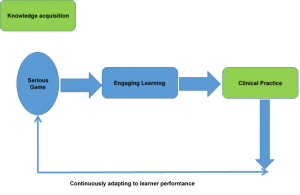
Figure 1: Date centric design philosophy for iterative training implementation
Case Study- Project ASMAN
Project ASMAN is an initiative aimed at reducing infant, neonatal and maternal mortality in India. It focuses on identification of critical conditions of mother during pregnancy and child birth (intrapartum and postpartum period) which emphasizes on user skills of identifying complication, knowing expected line of investigations, making correct diagnosis in critical situations and managing the patients.
What are some of the key characteristics, elements and features of effective games?
Let me explain this with the help of a case study of Bodhi’s ASMAN game.
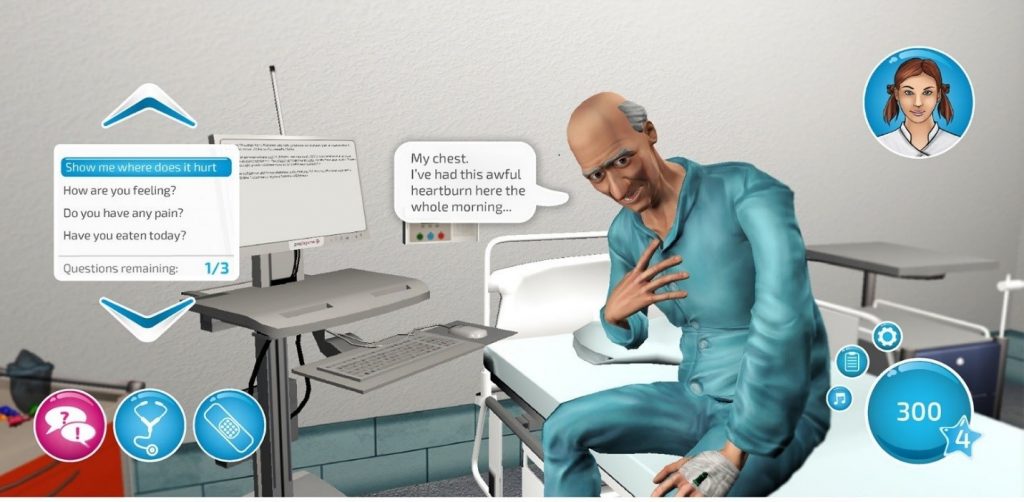
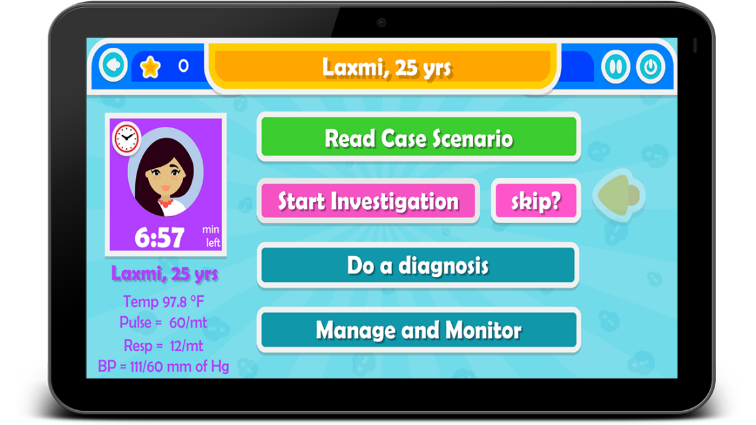
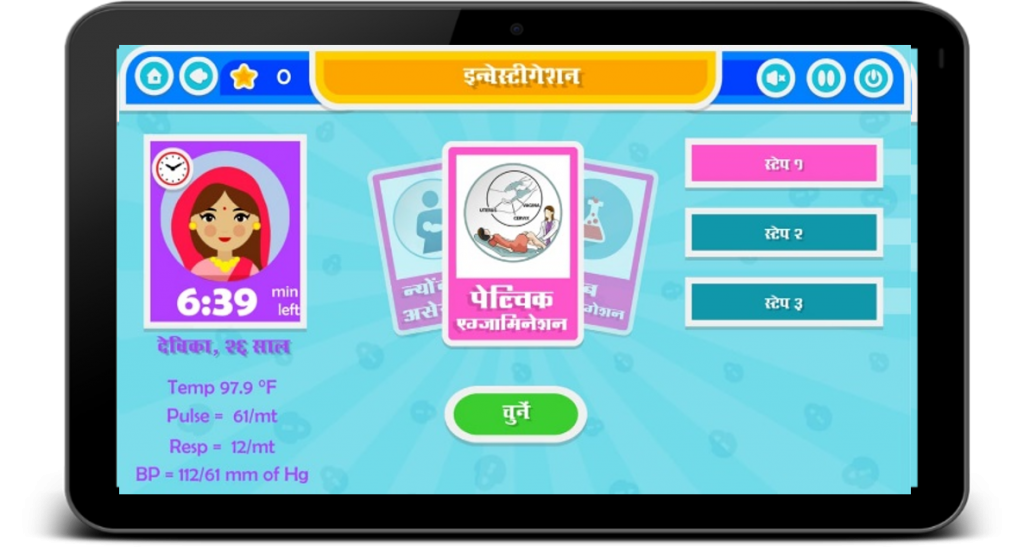
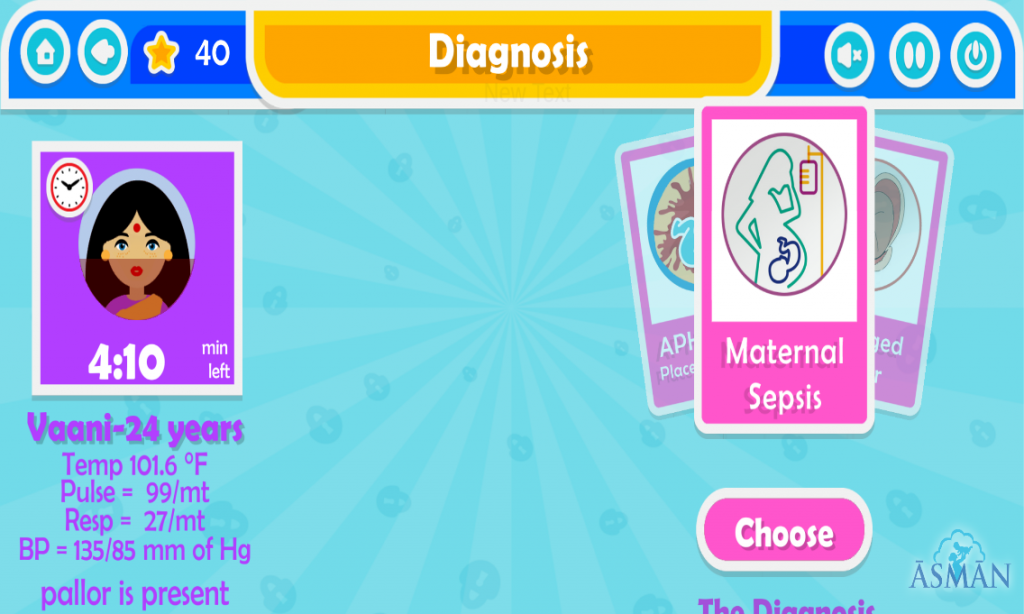
Problem Solving- Scenarios in the game allows the learner to perform variety of actions such as conducting investigation on patient, which helps them to understand the problem and warrants them to take action. For example as shown in the image the scenario describes a case where the data about the woman is supplemented. The user will initiate an action such as choosing the right investigation or making a diagnosis which will test the problem solving skills of the user and encourage him/her to think and act rationally.

Empowerment- Game provides an opportunity for the learner to feel empowered as it allows the user to choose options that will signify whether the patient condition will improve or deteriorate. As shown in the example here that the user can choose from list of investigations what to do. But not all the actions are warranted rather may waste the precious time when saving a patient. Choosing the right step in patient care can give a feeling of achievement as the user becomes confident about how to treat a patient in simulated real life scenario.

Thrill- The game gives a feeling of thrill as there is an urgency of action that needs to be taken within a limited time frame. As shown in the image with every passing minute the mother’s condition is deteriorating signified by the colour change in image of the woman indicating that her condition is deteriorating. User needs to make a quick decision to save the life. It gives a sense of rush and breaks the monotony.

Feedback- In the game the user chooses options and receives immediate feedback. A doctor appears and comments positively or negatively as per the choice made by the user explaining rationale behind the choice made. Additionally the user gets points for choosing the right option.

Context- The user in this game gets to learn about various conditions related to complications a pregnant woman might encounter and scenarios are specifically built around 29 such conditions that a woman might face during intrapartum and postpartum period.



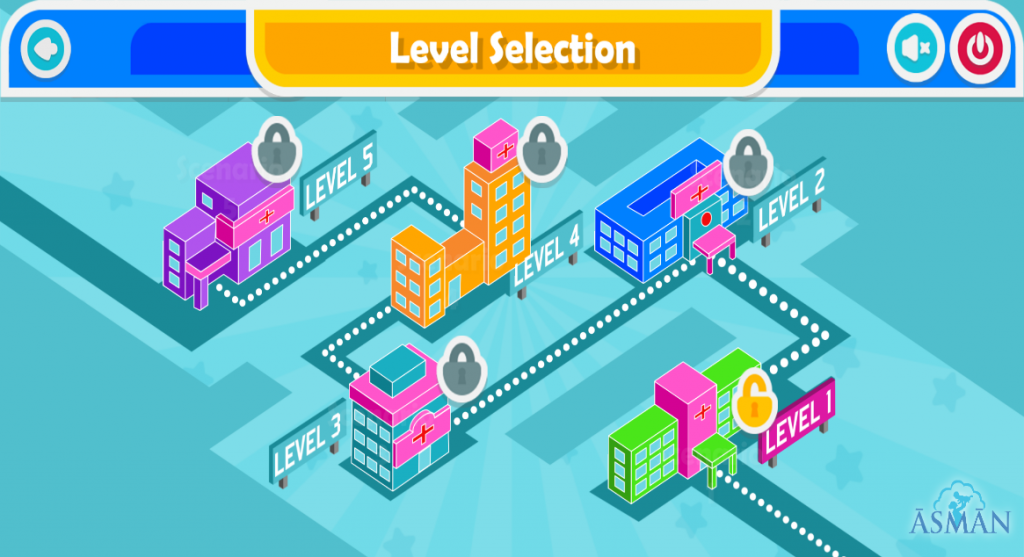
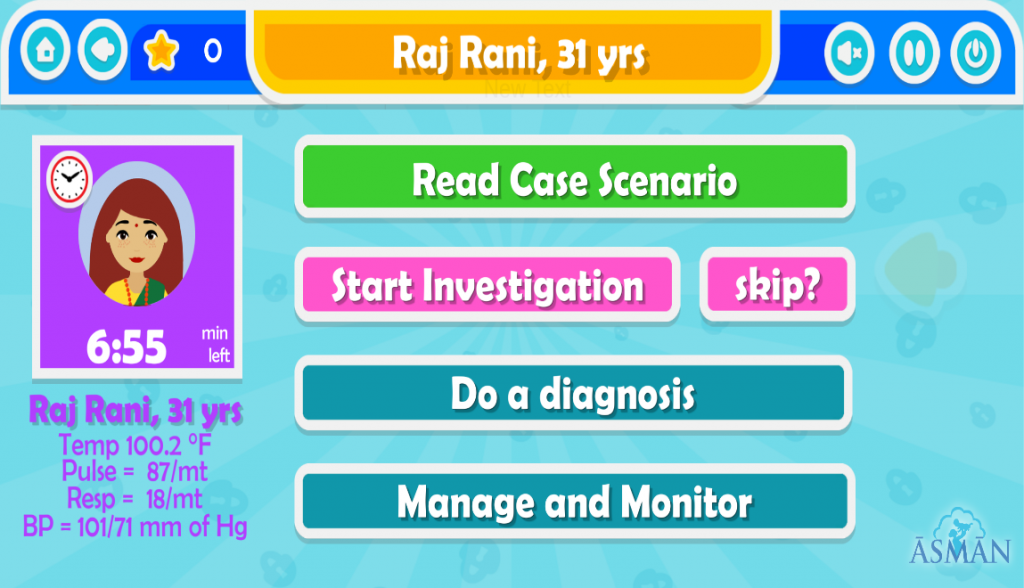
On-boarding- The ASMAN game is easy to understand as the learner moves ahead in the game. Whether it is entering the game, choosing the scenarios or the level they can access, it is indicated in a simplified manner. The learner is also guided which action is to be taken first for example as shown here the learner is first prompted to read the case before proceeding to choose the investigation and then further making a diagnosis followed by management of the patient. Game allows the new users to move steadily in the game.











Data analytics- The game provides option to capture key usage data like scores, time spent by the user on the app, number of trials in the web based dashboard to monitor compliance. The data captured provides opportunity to understand the strong and weak areas of the users that might need improvement. Based on the data captured there is a possibility to:
- Recommend learning path for every user
- Identify the high performing candidates and candidates who are about to dropout
- Generate actionable insights on clinical skills that need improvement
Partners- Project ASMAN
- The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
- MSD for mothers
- United States Agency for International Development (USAID)
- Tata Trusts
- Reliance Foundation
ASMAN Impact:
So far, 714 nurses across 8 districts in the Indian states of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh have registered on the app. Over the next 6-9 months the game app is expected to impact 2500-3000 nurses in these 2 states.


References:
1. Bauman EB. Theoretical and Practical Considerations for Serious Games Development. 2019 Sept 3. Slideshare. Available from: https://www.slideshare.net/ebauman/theoretical-and-practical-considerations-for-serious-games-development?fbclid=IwAR1KfwA6dCIbjQO2j-3aL9_CUDjjrmLgAxsJdifoAhrfjyGt9ietaehc05E
2. Huang LY, Yeh YC. Meaningful Gamification for Journalism Students to Enhance Their Critical Thinking Skills. International Journal of Game-Based Learning. 2017 April. 7(2):47-62. DOI: 10.4018/IJGBL.2017040104
3. Pront L, Müller A, Koschade A, Hutton A. Gaming in Nursing Education: A Literature Review. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2018 Jan/Feb;39(1):23-28. doi:10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000251.
4. Bigdeli S, Kaufman D. Digital games in health professions education: Advantages, disadvantages, and game engagement factors. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2017: 31; 117. doi:10.14196/mjiri.31.117






Leave a Reply